Leaving is a significant milestone in everyone’s life. Imagine yourself in your 60s, sitting on a comfortable armchair with a warm cup of coffee in one hand and a good book in another. You have achieved all that you wanted in life; all is good.
All of this can be possible only if you don’t have to worry about making both ends meet without a job. As perfect as it sounds, such a blissful retirement is not easy to achieve.
Aside from your individual retirement account (IRA) and individual retirement allowances, it would help if you considered both while preparing for retirement. Both offer tax-advantaged methods to save for your old days.
Pensions and IRAs both offer a plethora of favorable benefits in their ways, although different from each other.
In the article below, we have compared IRA and Individual retirement annuity (annuity) in-depth to deliver you a clear understanding of the possibilities you have.
What is an individual retirement annuity?
It is another asset offered by insurance companies, just like IRA. In this type of agreement, the insurance firm and the concerned individual ensure financial security for the individual at the time of retirement.

What are the main individual retirement annuities?
You can decide between the four main types of annuities for your retirement. These types have been categorized based on two factors:
- The time of receiving payments
- Annuity growth methods
Following are the four types.
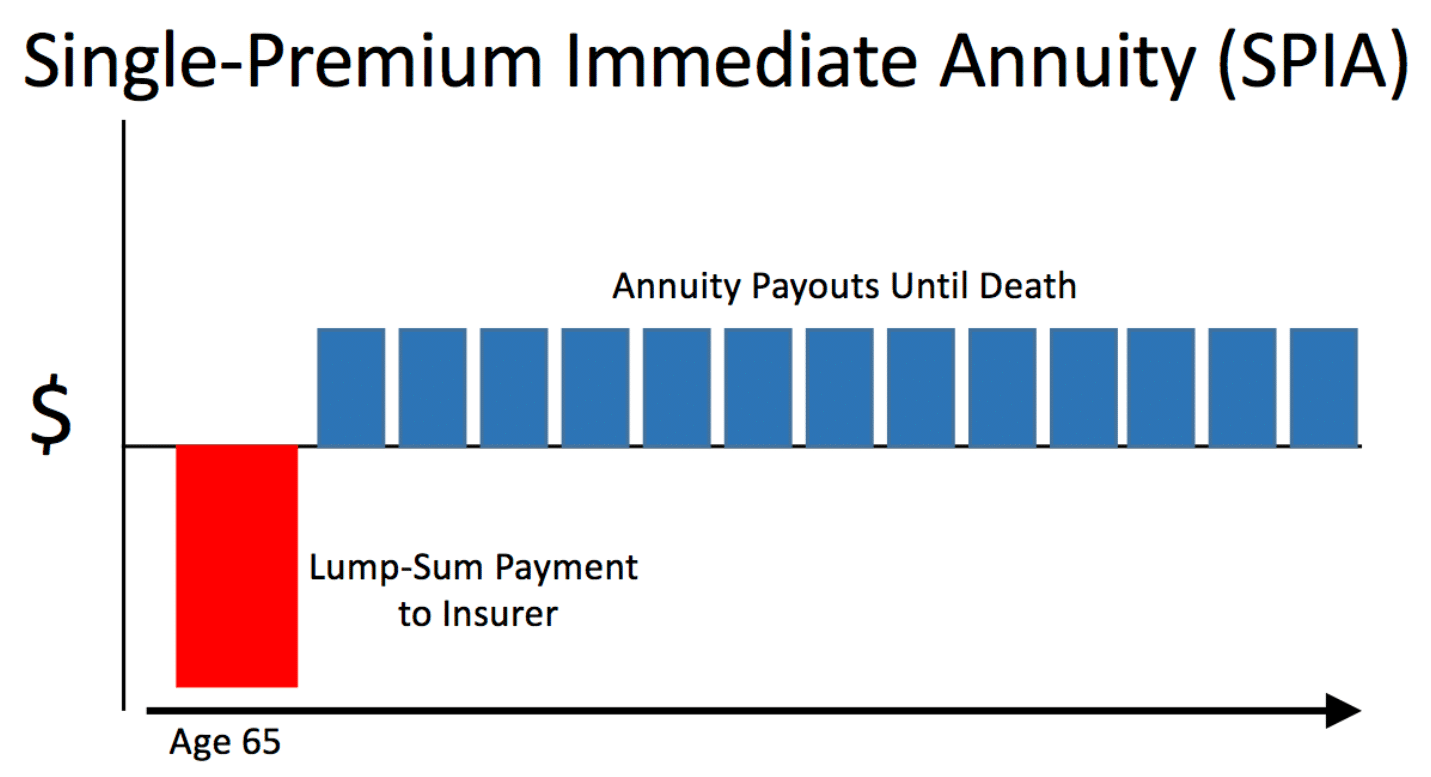
Type 1. Immediate
This is the most common type where you credit a single large amount to start getting back in smaller payments after one year of purchasing the annuity.
It is like getting a defined wage for the rest of your life without doing any job. Then, after your death, you can allocate the money to people and charities of your choice.
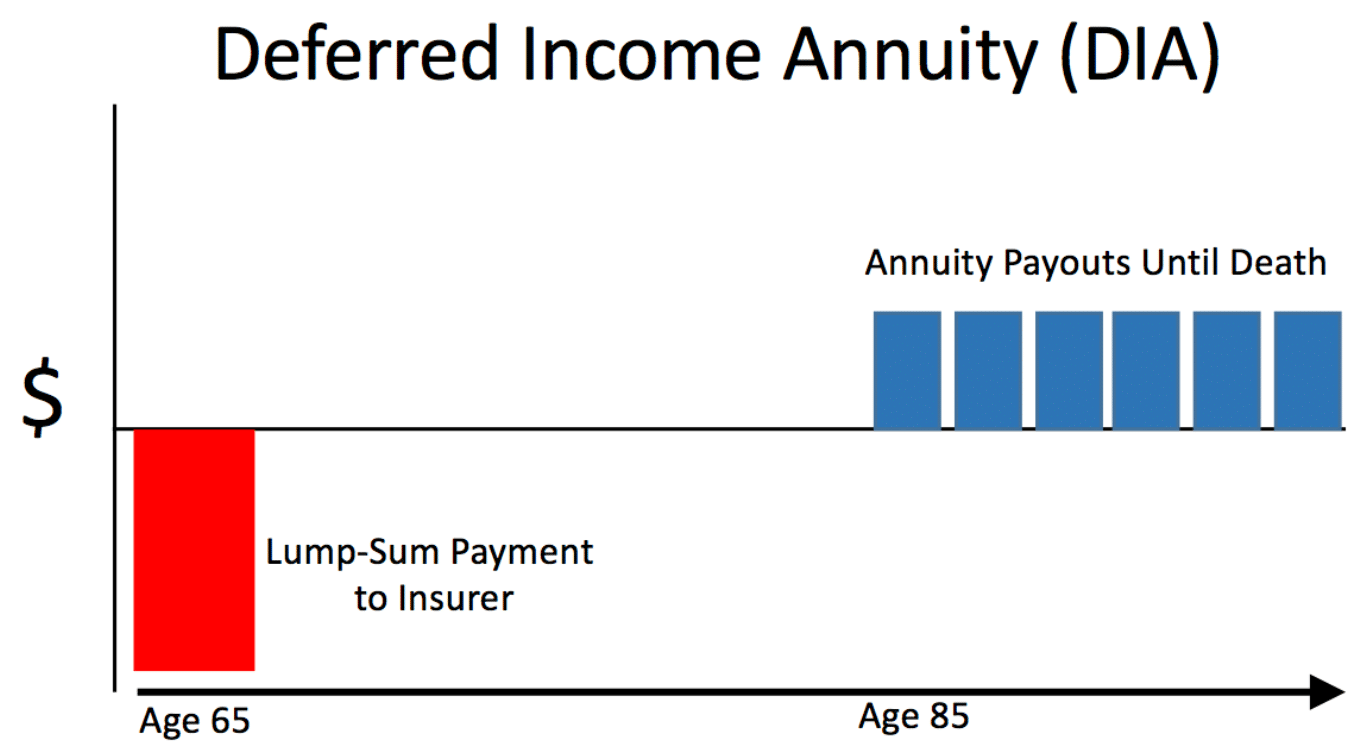
Type 2. Deferred
In the case of a deferred annuity, your insurer will invest a lump sum of your credited balance in a growth strategy of your choice.
Your money keeps on increasing until you decide to withdraw it. The best thing about it is that you can defer duties until you take the money out.
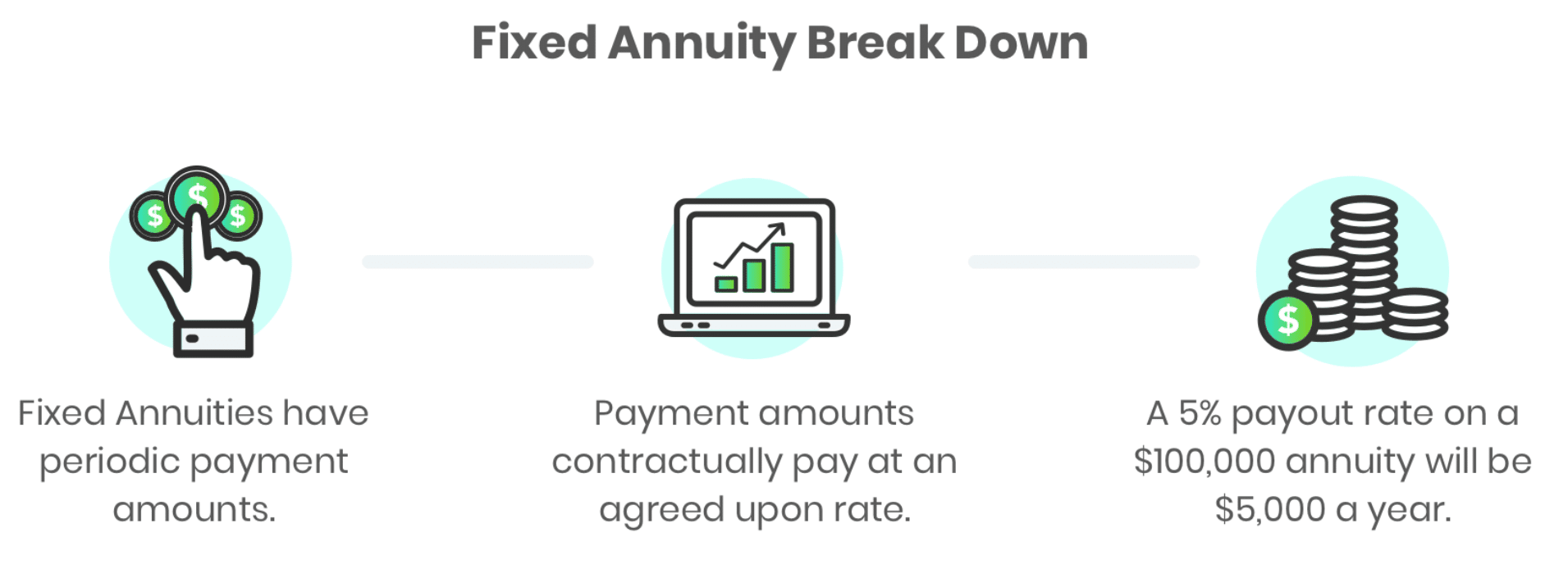
Type 3. Fixed
These are the simplest of all types. You get a definite interest rate liable upon the period that your pension lasts for.
The benefit of this sort of annuity is knowing the exact amount you will receive since everything is pre-decided and defined.
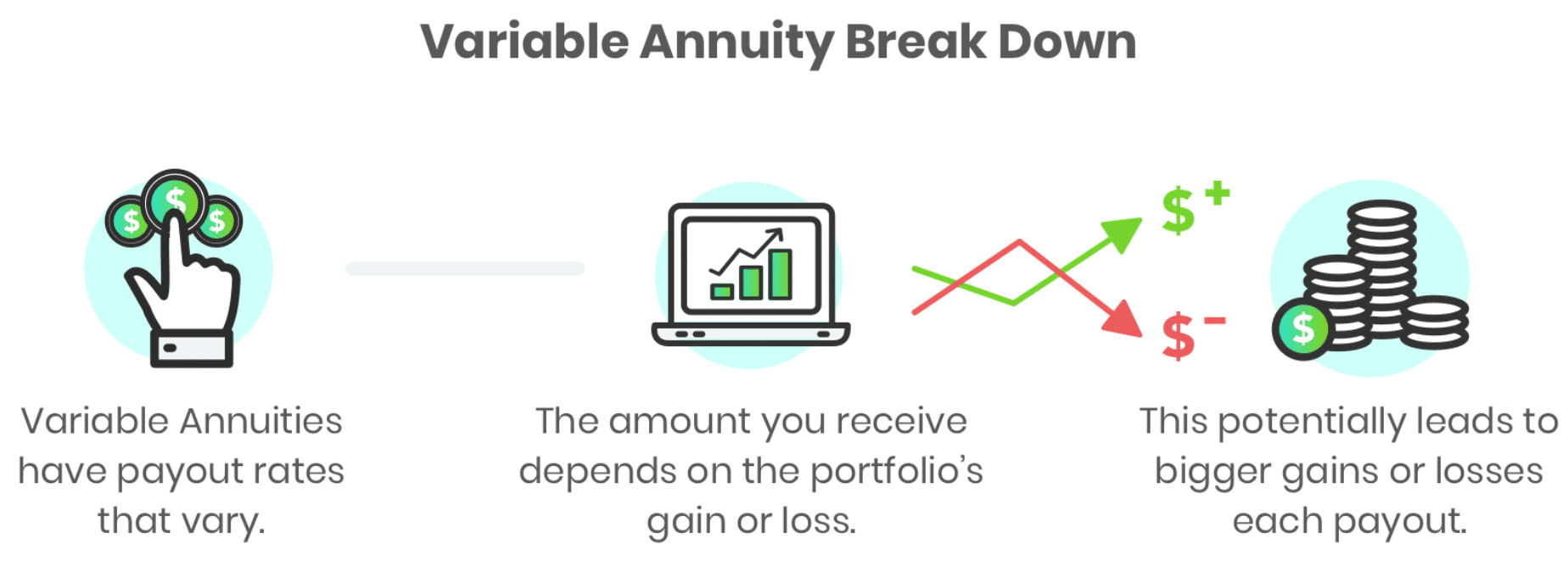
Type 4. Variable
This type has the most risks but the most rewards as well. Upon purchasing this annuity, your balance is tied to an investment sub-account. Therefore, the amount you will receive in the end depends upon the performance of your sub-accounts.
What is an IRA?
It is a type of recoverable account with tax benefits that provide financial security for the individual upon retirement. In addition, IRA stockholders can choose from various financial incomes like bonds, stocks, mutual funds, etc.
You can deposit only a limited amount per year and can’t withdraw it before you reach the average retirement age that is 59 ½.
However, if you withdraw the sum before the cited age, you will have to pay a 10% drawback and a tax bill.
Annuity vs. IRA
We will be linking annuities to IRA in terms of similarities and differences.
Similarities
Following are the comparison between both:
- Both of them offer tax-deferred or tax-free growth.
- Both of them pass the money down to the individual’s beneficiaries after their deaths.
- Both offer spousal continuance, which means the surviving spouse can continue getting tax-deferred benefits in case of death.
Differences
Following are the differences between both:
- IRAs have a limit on the maximum annual deposit, whereas annuities don’t.
- IRAs cost less than annuities.
- IRA is a convertible account that keeps retirement savings while annuities are investment products.
- IRAs aim to generate a more significant sum for you at retirement. Annuities ensure that you keep getting a steady but regular income after retirement until death.
- The risk in IRA depends upon how you invest your money, whereas the major risk in annuities is inflation.
Annuity rules
Given below are the guidelines for an annuity.
Payments
If you accept the reimbursement, it may be either a fixed amount or an adjustable amount. The investment process in secure annuities is completely out of your control, while variable annuities are at your disposal.
Taxes
Taxes are not valid on annuities until the time of withdrawal or when you start receiving payments. If the annuity was accepted with pre-tax capitals, the money would be taxed at the time of withdrawal.
You will still need to pay tax on the income if the annuity is credited with after-tax money.
Fees
It may vary for different categories of annuities. For example, dues for fixed annuities are much lesser than those for variable annuities since the former is comparatively more straightforward. The estimated average charge for a variable annuity is 2.3 percent of the agreement value.
IRA rules
Following are the rules for individual retirement accounts.
Payments
By 2021, the maximum limit for contributions is $6000. For people of age 50 or older, the limit has been extended to $7000.
Taxes
The balance can be tax-deductible in the deposit year; however, the investments that grow inside the account are tax-exempt.
Withdrawals
A 10% penalty may apply if you withdraw money before age 59 ½. IRS guidelines require those over 72 to begin withdrawing money from their IRAs.
Final thoughts
IRAs and individual retirement annuities are feasible options; however, what suits you best depends on your requirements. Evaluate your needs and go for the one that matches them to have a secure post-retirement life.



















Comments