There is no moving forward if you don’t know where you want to go. So the world’s most successful organizations systematically review their paths using strategic budgeting, planning, and forecasting at least once a year. This process is what allows them to keep it on track and perform better each year.
Whether you manage a company or any other kind of organization, you need to learn these strategies. In addition, you want to know how to elaborate and manage these procedures so you can take your organization to the next level.
So, go through this article to learn what you need to know about this subject.
Budgeting
The budget is the tool that gives financial viability to the planning phase. It’s how the expenses of the tasks and goals projected for the period are registered. Hence, planning and budgeting are not separate matters.
Instead, they often feedback each other and build a common path to the organization. The typical period used to plan budgets is the fiscal year. To build the budget at the beginning of each fiscal year, the people in charge check past years’ budgets to have a reference and make the budget as accurate as possible.
That’s why making the budget is a continuously ongoing task that requires constant amendment through the years to get as much precision as you can get.

Budgeting is about distributing the organization resources
Budgeting example
A business with multiple areas needs to watch how these areas work individually. The budget for each area should correspond to the result of each sector. When the budget is not carefully managed, there is a good chance that the most successful operation starts to lose capital to reinvest in poor-performing areas, which will hurt the overall value of the company.
Planning
If you ask the company executives, they will tell you that they want to make more money. But, if that’s all the executives say, they are not very good because a goal without a plan is just a wish.
Planning it’s what makes it possible to reach the goal. It draws the road map to your destination through detailed, measurable goals framed in a bigger context.
Organizational planning commonly spans three to five years and a few big goals. But it also contains many small achievable tasks that together build at least one of the main targets.
Let’s take a look at a planning model to learn better.
Planning example
A common planning model can consist of six levels:
- Vision
The ultimate goal of the long-term plan. All action should contribute to reaching that goal.
- Value
These are the fundamental principles that unite the organization’s members.
- Focus area
These are the categories in which the tasks are organized to achieve the vision.
- Objective
They describe more clearly the steps to reach the organization’s goal.
- KPI
The measures that allow you to know whether you are accomplishing your goals or not.
- Project
Temporary efforts with a start and end date. At the end of each one, a result has to be delivered.
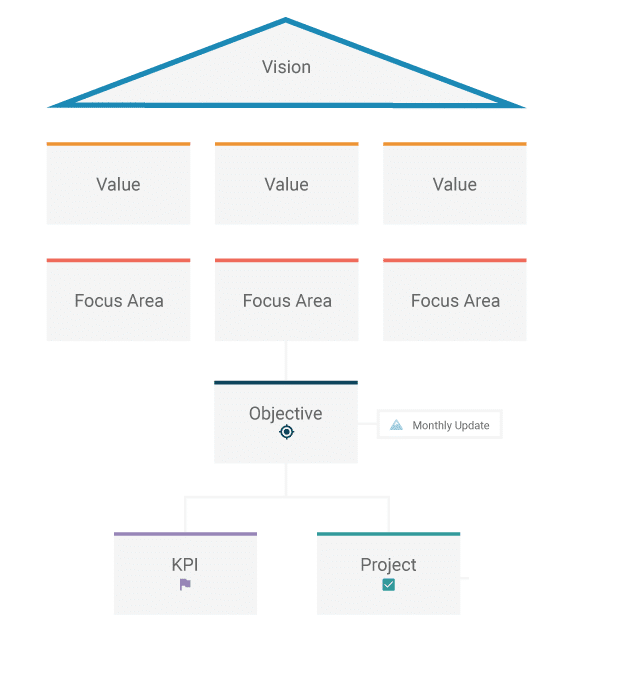
Planning is crucial for any organization
Forecasting
It is an art more than a science, and it’s the exercise of imagining how many different things can happen to divert the company from its course. But not just that. Once the team thinks about those diversions, the forecasters need to work closely with the planning and budgeting team to understand how each event affects the plan and the budget and how the company would respond.
Financial forecasters take recent events into account to understand what can go wrong, how the market behaves so the planning and budgeting team can adjust their strategies.

Forecasters review past data to evaluate different scenarios
Forecasting example
Let’s think about the case of a car company that produces many different models per year. This company also has to produce different parts and accessories to satisfy the demand of the consumers.
This is a difficult task, and there is no way to know exactly how many parts of each model will be needed by the consumers during the year. However, you can come close to the right numbers by reviewing past data and planning accordingly.
Budgeting, planning, forecasting: what is more efficient?
These processes are necessary for today’s organizations, and dispense with any could lead to disastrous results. Many academics attribute part of the 1929’s crisis to the lack of planning. However, since that time, the three processes have been adopted for companies worldwide. These companies experienced improvement from adopted techniques.
Since they are or should be tied together, it’s hard to define which one is more efficient. However, if you have to choose just one, that would be planning because it gives direction to the organization, and both budgeting and forecasting evaluate the goals in the plan. So, without a plan, there is no budgeting or forecasting.
Budgeting and forecasting process
You should not treat these processes separately. The budget always needs to have certain flexibility to adapt to the forecasted event. Also, initially, most of the budget is used to cover the expenses of the more probable events.
For example, at the beginning of the year, every company has an estimated demand, and they have to use that money to produce enough to satisfy this demand. If during the year the demand drops, the money designated to the production goes to other areas.
Streamline the budgeting, planning, and forecasting processes
The technological revolution we live in is changing everything around us. This has happened before, the introduction of computers changed the nature of the work and improved our efficiency. Nevertheless, we learned that organizational change is much slower than personal change.
Most companies still rely on Excel and avoid evolving to better solutions. Today, there are uncountable options for integrating different tasks from different departments to give a holistic approach to the team and avoid incompatibilities errors.
Main pros and cons
Of course, every approach has its advantages and disadvantages. Not every company applies these strategies, and some of them have a good reason for it. Let’s see the pros and cons of strategic budgeting, planning, and forecasting.
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
|
|
|
|



















Comments