Are you wondering why you have to pay taxes when your government already has a lot of money? Be aware that 50 percent of governments worldwide obtain around 80 percent of their funding from taxes. Without this funding, governments cannot perform their obligation to serve the citizenry through projects and services.
This post will touch on basic concepts of taxation to make you more knowledgeable about this topic. In particular, you will learn the most common terms being used in the field and the types of taxation being imposed. Learning about taxation is important and is relevant to your financial literacy education.
What is taxation?
Taxation refers to your financial obligations as a resident of a country. When you generate an income, you must give a portion of that to the government. Most countries require their residents to pay income taxes. However, the government imposes taxes on income and property, sales, investments, inheritance, and commodities.
Keep in mind that your tax obligation is mandatory. You have to pay your tax dues wherever you may be. At its discretion, the government can use force to compel citizens to pay their taxes.
Common tax terms
When learning about taxation, you must understand several technical terms because they are key to your understanding of the subject and because you will often come across these words. You better familiarize yourself with these terms right from the beginning.
Tax deduction
Getting a tax deduction is something that should delight you. For example, if you have a taxable income of $30,000 and qualify for a $5,000 deduction, your taxable income would go down to $25,000.
Tax credit
From taxpayers’ point of view, a tax credit is a good thing and slightly better than a tax deduction. The difference is that a tax deduction reduces the taxable income while a tax credit reduces the actual tax bill.
Tax refund
You will get a tax refund, for example, if you are an employee and your employer has withheld too much from your payroll to pay for your income tax obligation. The amount of the tax refund is simply the excess amount. Consider an overpaid tax as a loan with no interest to your government.
Exemption
An exemption refers to a person who depends on you for his or her basic needs. Those who can claim an exemption include yourself, your children, your spouse, or another dependent. An exemption is applied to your adjusted gross income to compute your taxable income. When you have an exemption, the effect is a lower taxable income, hence a lower tax bill.
Taxable income
The taxable income is the net income being used for computing your tax bill. The taxable income is a result of subtracting tax credits and tax deductions and considering exemptions.
Withholding
Withholding refers to the practice wherein the employer deducts a portion of your salary to pay for your income tax. This is an effective method used by tax-collecting government bodies to ensure working individuals pay their taxes. After one year, the collecting agency will review if you have paid your tax dues. If you have paid more than enough, the collecting body will return the excess amount to you as a tax refund.
Types of taxes
The government imposes the following taxes on residents of the country.
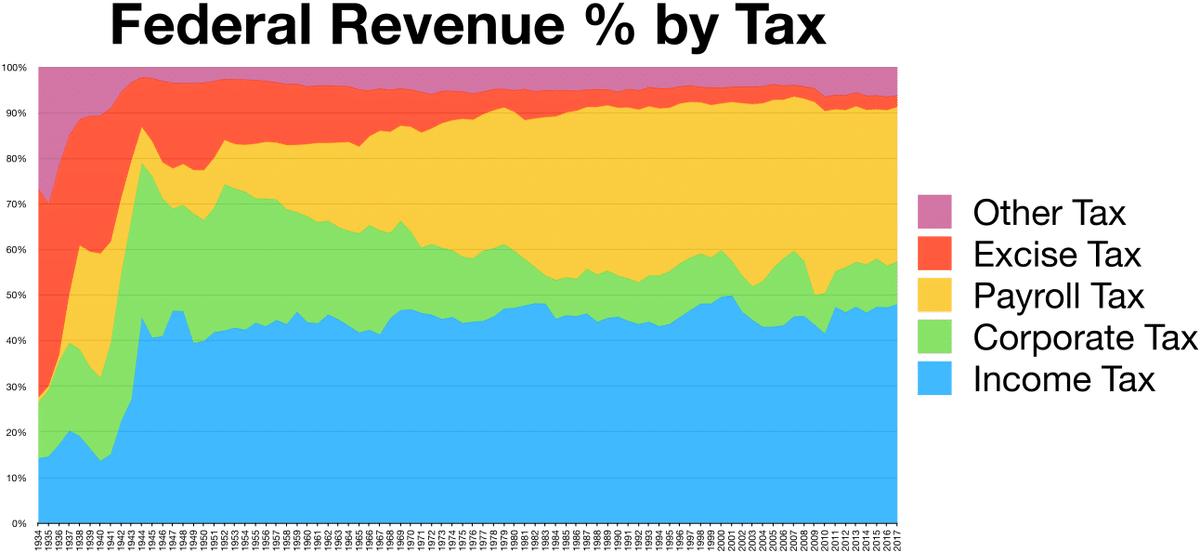
Income tax
Income tax is a tax applied to a person’s total income from various sources, such as salary, investments, and other income. As you gain more income, expect to pay more taxes as a result. Also, lower-income earners pay fewer income taxes than higher-income earners.
Corporate tax
Corporate tax is a tax applied to the total income of a business. The burden of paying this tax is considered in pricing products and services to generate income at the end of the year and after paying tax. To promote business, governments often apply corporate tax rates less than 30 percent.
Payroll tax
Governments impose payroll taxes on employees to pay social security trust funds. Typically, employers automatically deduct this tax from employees’ income and pay the tax on their behalf.
Capital gain tax
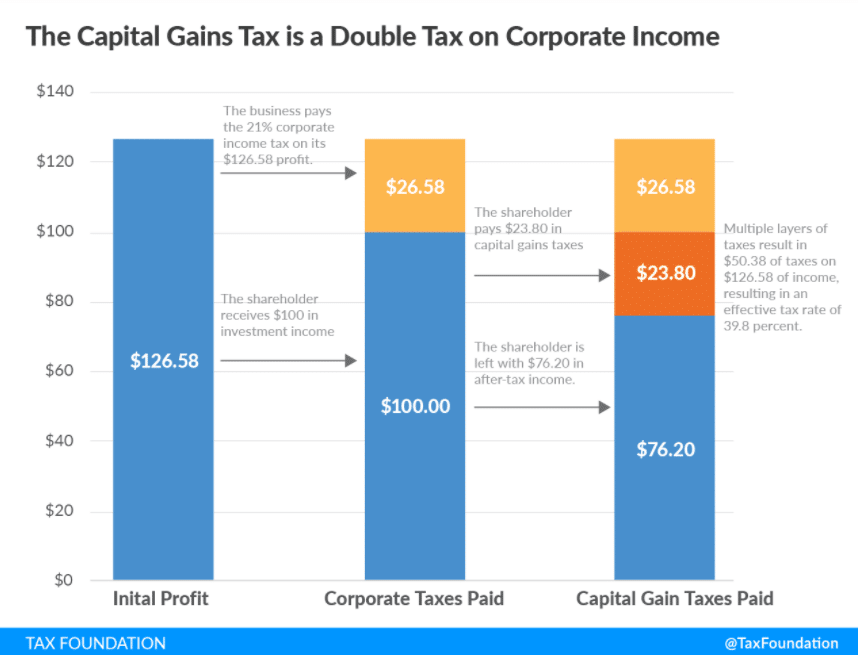
Capital gain tax is applied to capital assets, covering investments and personal properties such as houses, stocks, cars, bonds, and jewelry. Capital gain applies when the value of an asset appreciates, such as a stock share price rising. Therefore, when you invest in stocks and hold your portfolio for the long term, you will pay tax on the return of that investment.
Property tax
Governments impose payroll taxes on employees to pay social security trust funds. Typically, employers automatically deduct this tax from employees’ income and pay the tax on their behalf.
Sales tax
Sales tax is a tax imposed on the consumption of goods and is an effective way to collect taxes. The consumer may not be aware of it, but every item purchased includes tax payment. This type of tax covers many consumable items, such as clothing, food, groceries, construction supplies, etc.
Value-added tax
Many countries in the world use value-added tax (VAT). This tax is similar to the sales tax, which the consumer must pay. The difference is that consumers and producers share the burden of paying VAT.
Excise tax
Excise tax is a tax applied to certain commodities such as cigarettes, alcohol, fuel, etc. Some countries apply excise tax to take advantage of the behavior of consumers, for example, frequent alcoholic drinkers. Because many people drink alcohol, governments can generate revenue by applying taxes on alcohol. Applying higher taxes on alcohol or cigarettes is justified based on limiting substance use all for the individual’s good.
Final thoughts
Now you have learned about the different types of taxes and some standard terms in taxation. You can use the lists here to dig deeper into each type of tax and expand your knowledge on taxation topics one term or two at a time.




















Comments