Understanding a 401k plan is already confusing in itself. How much more is Roth’s 401k? While the two retirement plans look complicated on the surface, it is not the case when you get down to the details. Being under the same category (i.e., 401k), these retirement options are pretty similar. However, there are several differences worth knowing.
Nowadays, more and more companies are providing employees access to Roth 401k. If you have this plan in the workplace, it means you belong to the majority. In the last five years, the number of companies providing Roth 401k as a retirement plan option has grown by 32 percent.
In 2021, about 75 percent of workplace retirement plans offered a Roth 401k option. In addition, the younger generation is beginning to tap into this retirement option. Sixteen percent of employees who save for retirement through a Roth 401k are millennials.
The question that still lingers is this: which one would you choose from given the option between regular 401k and Roth 401k? To make the crucial decision, you need to understand both options in more depth. Let us look at how they differ in the next section.
401k: Roth vs. traditional
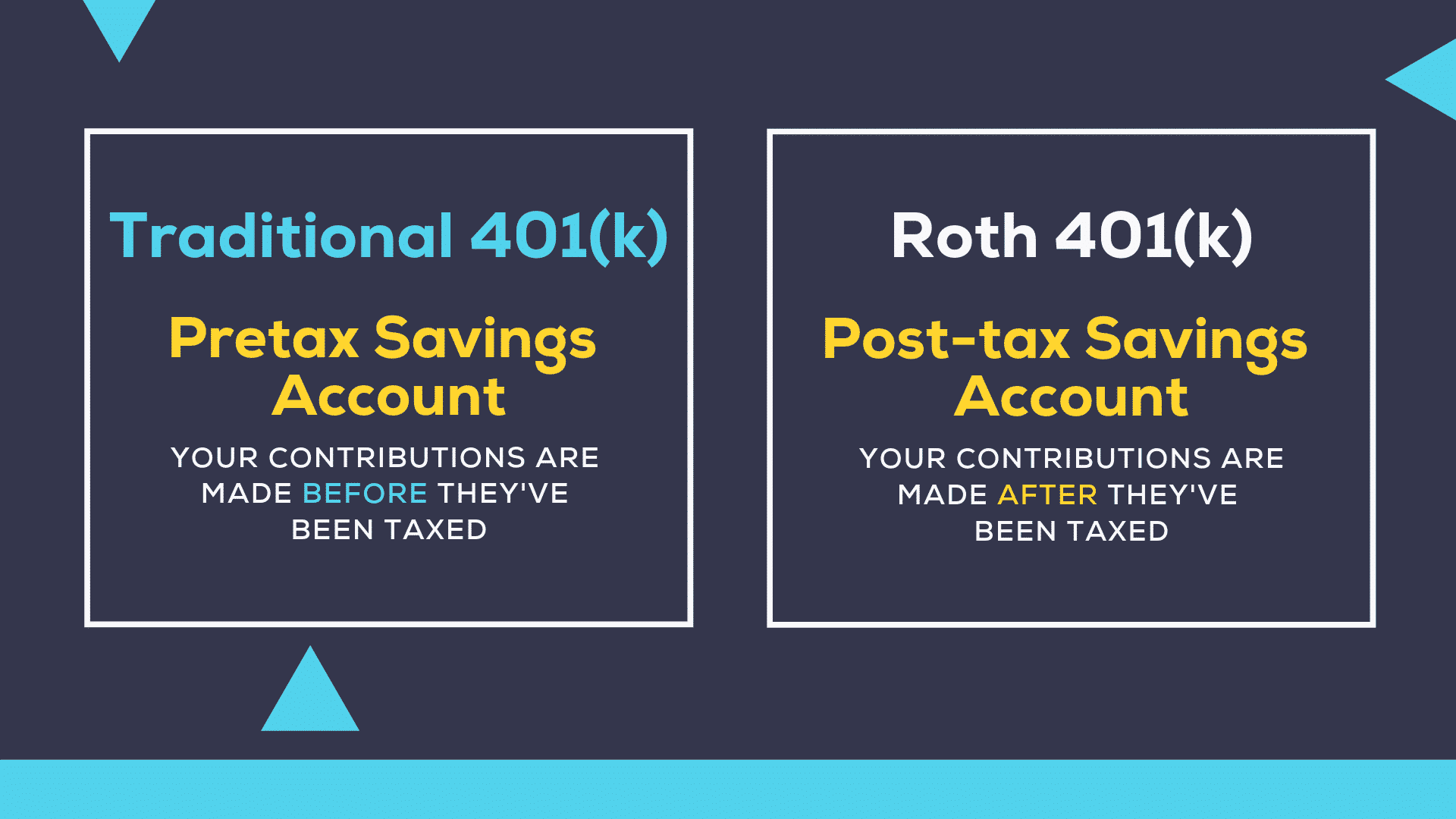
A traditional 401k involves saving money when tax has been deducted from the paycheck. Although this leads to lower taxable income, you will have to pay your tax obligations in the future when you retire and start cashing out money.
A Roth 401k involves after-tax contributions, meaning tax is applied to your income before you take out funds to put in your Roth 401k. You have no tax break now, but you save that for later. When you retire and start cashing out income from your Roth 401k, you will not have to pay any taxes. Just make sure that you have held the account for five years or more by then.
Both types primarily vary on the tax benefit. The good news is that you do not have to choose one of the two options. You can contribute to both plans. If you take this route, see that the total contribution does not go beyond the maximum limit set for the applicable year. In 2021, the maximum yearly limit is $19,500.
Top 3 reasons to use a Roth 401k
Is it right for you? Here are the top three reasons why you should use this plan:
- If you have a low tax rate now and expect to be in a higher tax rate on your retirement, the Roth 401k is your best bet. This is often the case for the younger population.
- If most of your retirement income (e.g., pension, social security, etc.) and retirement savings are directed toward tax-deferred securities, this variant makes much more sense.
- If the addition of Roth savings to the taxable income would not adversely affect your tax obligations, consider using a Roth 401k.
Top 3 reasons to use a traditional 401k
Wondering if a traditional 401k is suitable for you? Here are the top three reasons why you should opt for this plan:
- You belong to a high-income tax bracket right now, and you expect to go down a bracket or two on your retirement.
- You are earning high, and you have already diversified taxes for your assets, maybe from an old Roth 401k, Roth IRA, or a brokerage account.
- If you do not want to include contributions in your taxable income, then consider a traditional 401k.
Pre-tax and after-tax traditional 401k
The manner of treating tax for distributions of a regular 401k is quite simple. When you contribute, the funds are taken from your gross salary. As a result, your taxable income has greatly been reduced, so does the income tax paid.
Typically, regular income tax applies to distributions from such plans, and the tax rate is based on your tax bracket for the year the withdrawal is made. This means that tax payment is deferred at the moment but is due for payment in the future when distribution begins. Thus, a traditional 401k plan is a tax-deferred account.
Pre-tax and after-tax Roth 401k
The Roth 401k lets you contribute money after tax is taken from your paycheck. As a result, you will enjoy tax-free distributions later on in your retirement. This means that this plan is an after-tax account.
The advantage of after-tax savings is that you will avoid the possibility of paying higher taxes in the future in case your tax rate goes up. This is the problem inherent in pre-tax 401k accounts wherein taxpayers will have to pay more significant taxes on each withdrawal because their tax rates have moved higher.

The above image shows an example calculation for each type of tax treatment using a yearly salary of $50,000.
Roth 401k vs. traditional 401k: main advantages and disadvantages
Roth 401k
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| If you do not qualify for a Roth IRA due to your high income, a Roth 401k provides the same tax benefit. | You cannot cash out funds from this plan if you hold the account for less than five years. |
| Your beneficiary could enjoy tax-free distributions as long as your Roth 401k is five years or more when you pass away. | If your company offers both plans, your employer’s counterpart contributions will be reflected in the traditional 401k regardless if you select a Roth one. |
| Because contributions for Roth 401k are taxed upfront, the investment and profits are all yours to enjoy. | You will not enjoy a tax break while building your retirement account. |
Traditional 401k
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| You will enjoy a tax break today and put off paying taxes until you retire. | When you pay taxes at retirement, your tax rate at that time could be higher than today if you earn more income later. |
| Gains or profits made by your investments are tax-deferred. | Your withdrawals during retirement are said to be ordinary income, hence subject to income tax. |
| You will save money on taxes if you belong to a high tax bracket right now and expect to earn less when nearing retirement. | If you choose this plan and you do not save the tax savings, the growth of a Roth 401k will outpace that of your traditional 401k. |




















Comments