Often you come across a situation where you have a winning position, but all of a sudden, the price starts moving oppositely.
You start to panic, exit your losing trades, and end up depleting your account. So, is there a way to not end up losing?
Yes, there is. It’s called hedging. This guide will explain what hedging means in forex and how to limit the risks by applying five techniques.
What does hedging mean in forex?
In FX, hedging is the process of limiting your losses by entering into one or more trades that can counterbalance your existing position. Hedging’s primary goal isn’t to make your losing trades into winning ones; instead, it’s to keep them at a manageable level.
When you do hedging, you open a position in the opposite direction of your current position. So, when your first position turns red, your new position will turn green.
You are probably thinking, how about I close my position and re-enter later? Well, you can do that, but with hedging, you can keep your first trade open while profiting from your second position.
Afterward, you can exit the second trade, and when the market moves in favor of your first position, you can leave that trade profitably too.
Forex hedging example
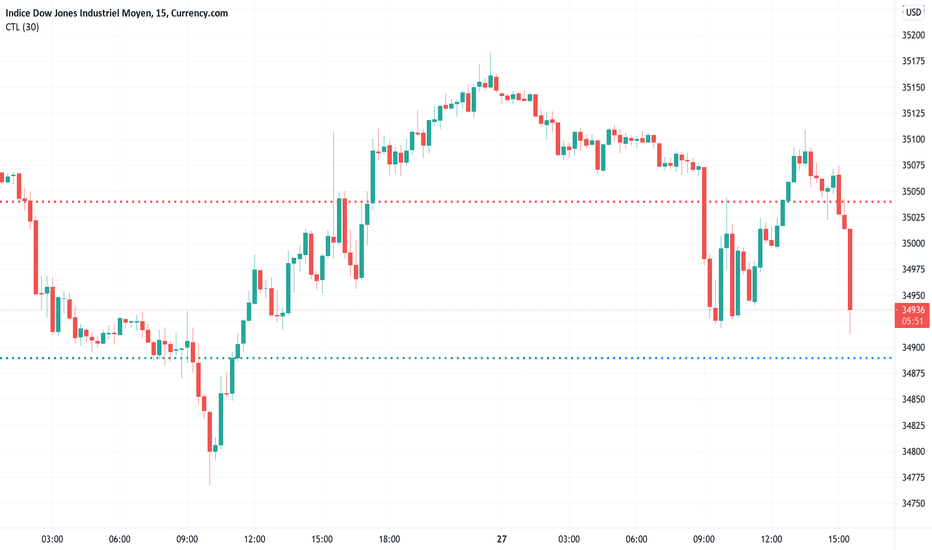
Let’s illustrate this with an example. The chart below shows that the price went up, dipped, and finally climbed up. So, for hedging, you’ll open the buy position initially, then when the price declines, you’ll go short, leave the short position, and continue trading with the first one.
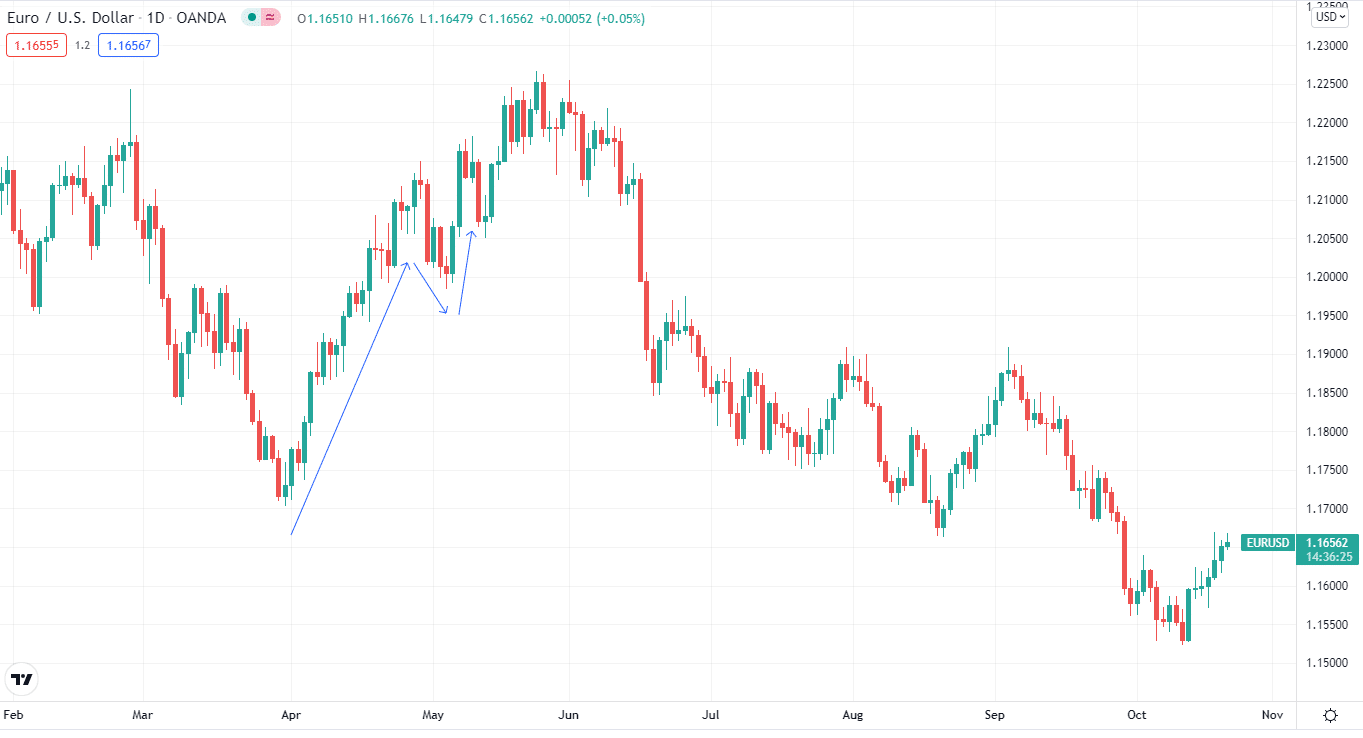
Hedging example
How to hedge currency risk?
Now hedging isn’t something that is designed for beginner traders. Because it requires a deep understanding of the market to apply hedging techniques, it’s a high-risk, high-reward kind of situation, so if you don’t enter or leave at the right time, you can face significant losses.
However, there is always a way. If you are a beginner, you can learn the market movements and mitigate your currency risk.
Top five tips to hedge forex
Here are some of the strategies you can use for forex hedging.
Tip 1. Do direct hedging
As the name suggests, direct hedging is when you already have an open position and apply for the opposite position when the market starts moving in the other direction. The example mentioned above was a form of direct hedging.
The idea of direct hedging is to gain profit or mitigate your risks. The second position will cover all the losses you had from the first trade. This form of hedging applies when you have a long-term position and want to short hedge sudden market swings or a news event.
Ok, let’s define this with an example.
Suppose you want to go long on EUR/USD, and you want to hold this position. But there’s a major news announcement coming, so you figure out that it’ll cause uncertainty. So, you open a short position for a few days and then close out that position. But your initial position will remain long.
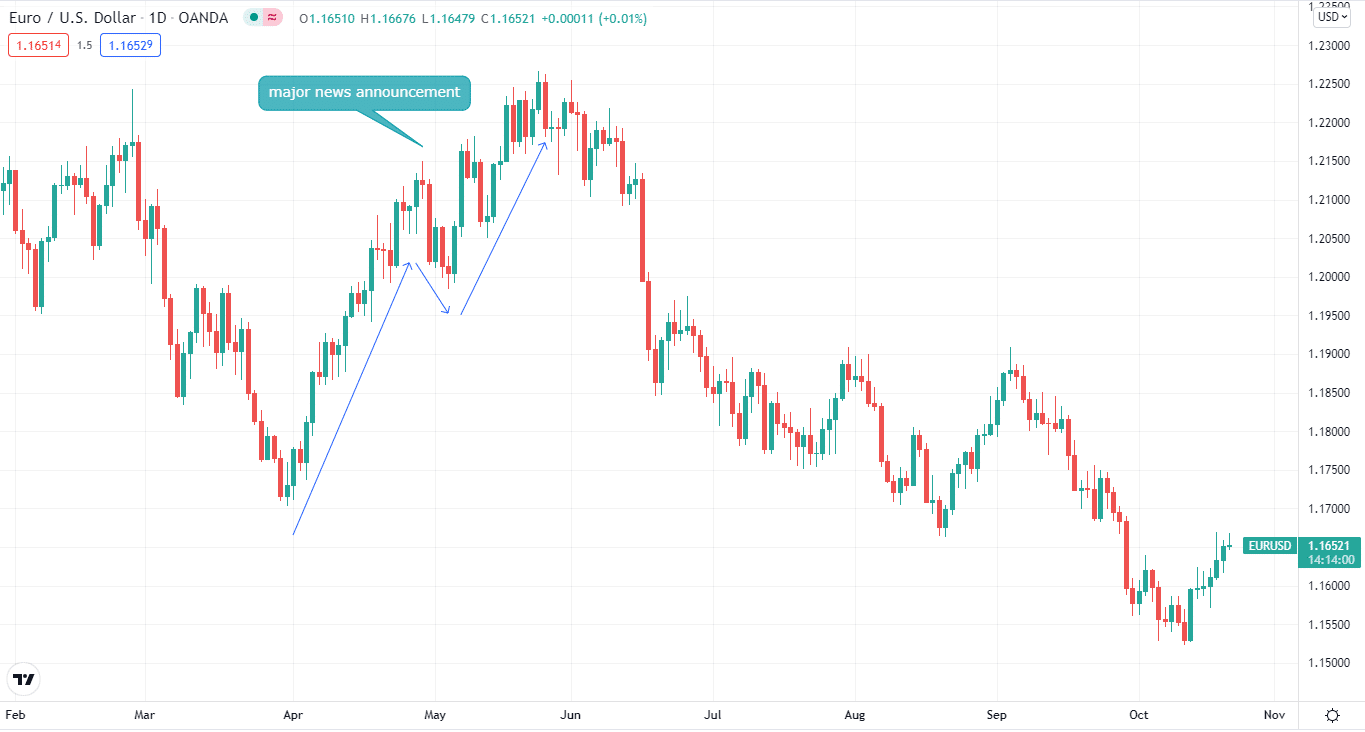
Direct hedging
How does this happen?
Markets can move in certain trends for an extended period. However, major news releases or market volume can disrupt this trend.
How to prevent the fault?
By using a direct hedge, you can keep your initial position while dealing with short-term fluctuations.
Tip 2. Go with indirect hedging
Currency correlation is a common phenomenon in forex trading. It means that two currencies behave relatively. They can have a positive (moving in the same direction) or negative correlation (moving in the opposite direction).
For instance, GBP/USD and EUR/USD have a positive correlation. So when one of the pairs goes up, the other will also trend upwards. This is because of GBP and EUR political and geographical scenarios.
So, if you had a long position on GBP/USD, you could hedge it with a short position on EUR/USD. For example, on the below charts, you can see that we took a long position on GBP/USD while we hedge it by taking a short position on EUR/USD.
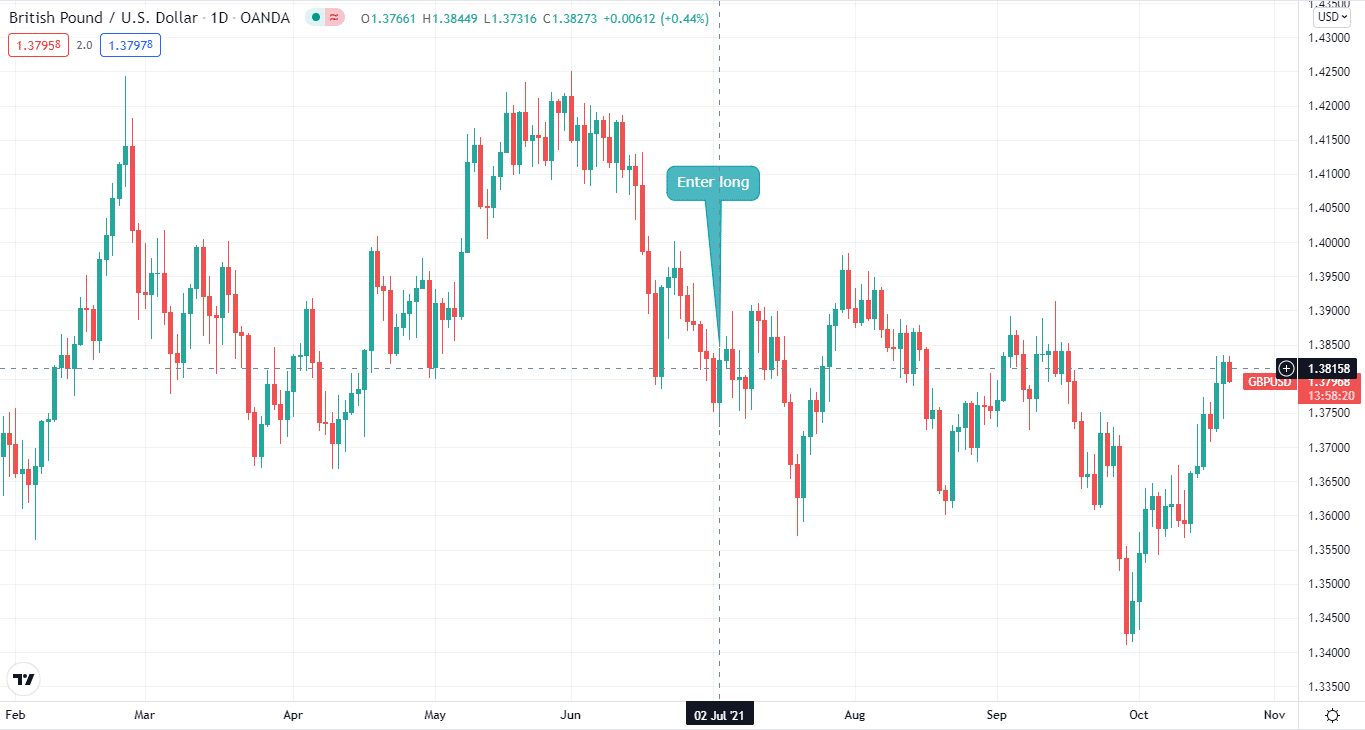
Indirect hedging: GBP/USD chart
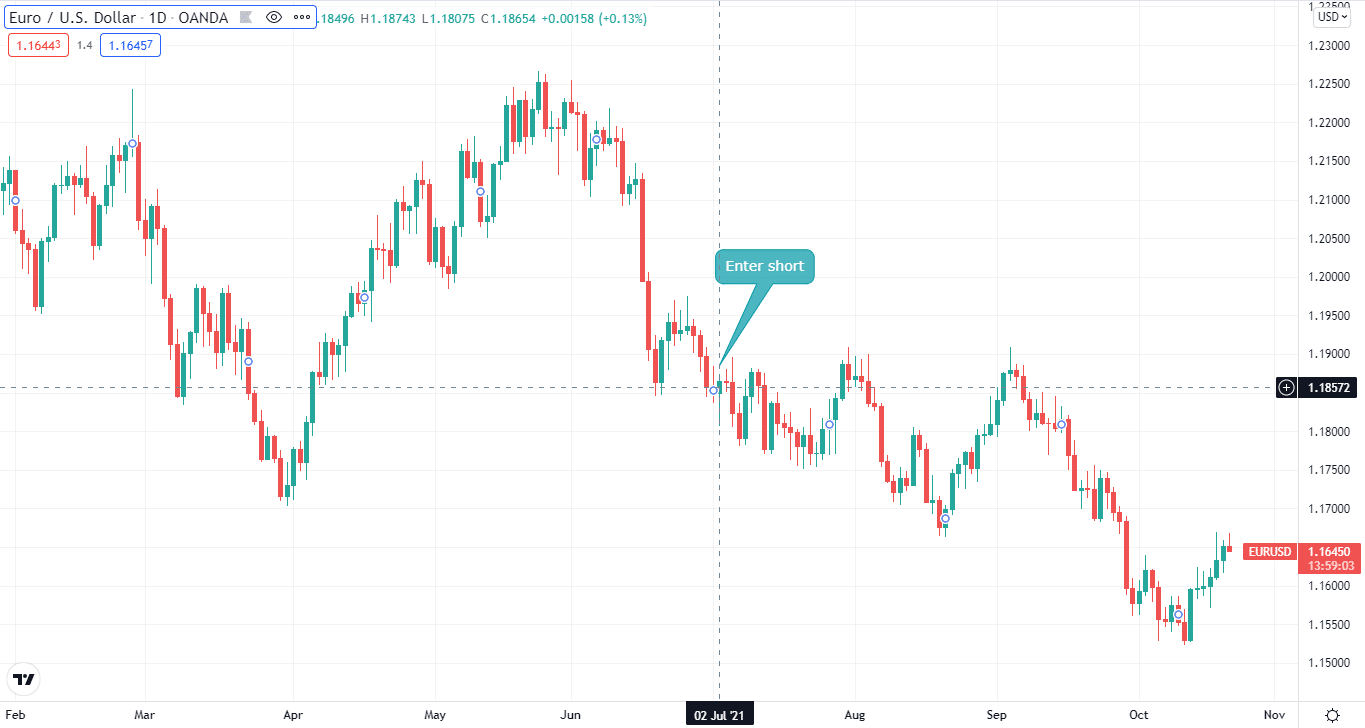
Indirect hedging: EUR/USD chart
How does this happen?
Currencies tend to show the same characteristics due to political and geographical reasons. As a result, they can move in the same or opposite direction.
How to prevent the fault?
When two currencies have a positive correlation, then for hedging strategy, you can go long on one pair and short on the other pair.
Tip 3. Apply options
A forex option is a contract that provides you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a certain price (strike price) on a predetermined expiration date. Puts, which give you the option to sell a currency, and calls, which give you the option to acquire a currency, are the two forms of options.
Let’s say you decide to take a call option and buy EUR/USD, but think that the price may fall. You can go with the put option and sell EUR/USD to profit from the falling price and mitigate the risk.
How does this happen?
Options work according to a set expiration date. The contract will expire on your chosen date.
How to prevent the fault?
If your hedge didn’t work out, you’d lose the premium you paid to begin the position if you let your option expire worthless.
Tip 4. Through forwarding contracts
Currency forwards are similar to options, as they allow you to swap a currency at a specific price at a particular date in the future. Unlike options, the contract must be fulfilled at the end of the term, either in cash or in person.
How does this happen?
Like options, a forward contract can provide you with an expiration date, and you have to settle it on a cash on delivery basis.
How to prevent the fault?
Hedging using forex forward contracts is a good way to lock in a price in advance and protect against market volatility.
Tip 5. Trade with other CFDs
CFDs — indicators and signals
You can also use the option of trading in other markets like stock or commodities to limit your forex risk exposure.
There are plenty of CFDs (contracts for difference) available depending on your broker, and if you are losing on a forex trade, you can hedge in the other market.
How does this happen?
CFDs allow you to own an underlying asset without its physical ownership. As a result, you can buy or sell just like forex.
How to prevent the fault?
You can diversify your investment portfolio and hedge against your forex losses by placing trades in other markets.
Final thoughts
If you are looking to trade in the forex market, then direct hedging is your best bet. It’ll allow you to limit the risk of your initial position, close out your second trade, and continue with your first one.
However, as mentioned, you have to understand market movements to try hedging thoroughly.


















Comments